About Treatment
The search for more sparing methods of surgical treatment of diseases of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses was aimed at minimizing surgical trauma and preserving the normal anatomy of the intranasal structures.
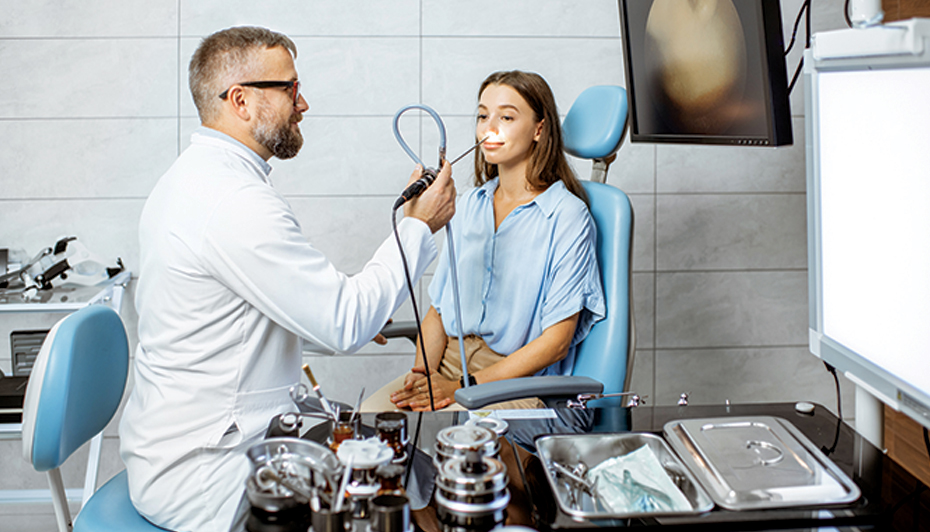
The development of functional endoscopic rhinosurgery is associated with the development of rigid endoscopes. The endoscope is an optical system with a built-in fiberglass light guide, enclosed in a metal sheath. The resulting image can be evaluated directly through the lens or, if there is a video camera, on the monitor screen. At the same time, by increasing the area under study, it is possible to identify the most minimal changes, simply by bringing the end of the endoscope closer to the suspicious area. The ability to save the ongoing endoscopic examinations and operations on disk allows you to create a base for assessing the dynamics of the treatment.
Endoscopic surgery of the paranasal sinuses - FESS- Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery is by far the most optimal method of surgical treatment of chronic sinusitis. Performing such operations requires not only a good knowledge of the endoscopic anatomy of the intranasal structures, but also the ability to perform endoscopic manipulations bimanually.
Of great importance in the development of diseases of the paranasal sinuses are pathological changes in the region of the middle nasal passage, where their fistulas open. The goal of surgical treatment for chronic maxillary sinusitis is to create an adequate communication between the sinus and the nasal cavity. This restores ventilation and sinus drainage. Through an expanded natural anastomosis, all pathological contents from the sinus can be removed - purulent discharge, foreign body, cyst, mucocele, polyps.
Visual control allows to preserve unchanged structures as much as possible. For the treatment of frontal sinusitis, it is necessary to restore ventilation of the frontal sinus through the natural frontal-nasal canal. For ethmoid and sphenoid sinuses, the same principle is used: if necessary, the maximum number of affected cells of the ethmoid labyrinth is opened, but not all of them. The preservation of not only normal but also pathologically altered mucosa is one of the concepts of endoscopic sinus surgery. It has been shown that the restoration of normal ventilation of the sinuses promotes the regeneration of the mucous membrane.
It is necessary to take into account the fact that the development of chronic sinusitis may be associated with pathological changes in the nasal cavity: curvature of the nasal septum, hypertrophy of the middle or inferior turbinates. In this regard, in order to achieve a good effect in operations on the paranasal sinuses, the nasal septum is corrected, the destruction of the inferior turbinates, and partial resection of the middle turbinate.
To stop nosebleeds in the postoperative period, sponge tampons are used. Such a tamponade is well tolerated by patients, it is easily and painlessly removed from the nasal cavity on the 2nd day after the operation.
Using FESS method allows not only to restore normal nasal breathing, but also to preserve the anatomy of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses as much as possible. Such operations are easily tolerated by patients and do not require a long hospital stay. After the intervention, the recovery period takes about a week.
Postoperative care of the nasal cavity is also important - removal of clots and crusts, the appointment of anti-inflammatory, anti-edematous and antibacterial therapy. This prevents adhesions and promotes better healing.
-
Procedure Duration
2-4 hours
-
Hospital Stay
One Night
Possible indications are anatomical changes (for example, a deviated nasal septum), when polyps or mucous membranes interfere with natural ventilation processes, or tissues are already seriously damaged by ongoing inflammation.
Intervention is necessary for complications of sinusitis, for example, when inflammation spreads into the eye socket or brain structures.
However, before the surgical treatment of chronic sinusitis, a complete diagnosis must inevitably be carried out, in which the possible causes of the disease are identified.
Most Common Indicaions For Fess
Chronic rhinosinusitis
Recurrent sinusitis
Polyposis of the nose
Antrochoanal polyp
Paranasal sinus cysts
Foreign bodies of the paranasal sinuses
Tumors
Mucocele of the paranasal sinuses
Liquorrhea
Orbital decompression (Graves ophthalmopathy)
Decompression of the optic nerve
Dacryocystorhinostomy
Choanal atresia
Nosebleeds
Strongly dependent on individual characteristics and the area of the sinus:
Formation of blood clots (hematoma).
Decreased sense of smell.
Trigeminal irritation or trigeminal neuralgia.
Injury to the tear duct.
Orbital hemorrhage.
In the first few days after surgery, the nasal airway may be blocked due to swelling, which leads to a feeling of stuffy nose. In addition, bloody "crusts" can form on the nasal mucosa and increase the itching sensation in the nasal cavity. Rare complications include re-bleeding, odor disturbance, increased neuralgic pain, inflammation due to accumulation of secretions, and minor bruising under the eyes.
The ability to inspect the affected area and targeted removal of only affected tissues and preservation of intact structures;
Preservation of the sinus mucosa, respectively, and preservation of sinus function;
Lack of external incisions;
Creation of physiological drainage of the sinuses through natural fistulas;
Less likelihood of complications.
Patient should be examined by an ENT surgeon to make an exact diagnosis, exclude other ENT diseases and determine clear indications for surgery;
Compulsory CT scan of the nose and paranasal sinuses, for individual selection of the type and volume of intervention. CT also helps surgeon navigate during the operation;
After ENT doctor has confirmed the need for the operation, it is necessary to undergo a general preoperative examination on an outpatient basis and obtain a therapist's conclusion about the absence of contraindications to the operation.
On the first day after endoscopic surgery, there are special spongy tampons in the nose, which sometimes cause a feeling of pressure and headache - these symptoms are normal and quickly disappear after the tampons are removed;
Patient spends a day in hospital and the next day after the operation goes home
Patient visits surgeon on an outpatient basis: to remove tampons, rinse the nose and control healing - there will be 2-3 such visits after the operation;
In the first week after the operation, patient is not recommended to drink hot and alcoholic beverages, take a hot shower, exercise;
During the first week after the operation, it is better to follow a home regimen, to avoid colds;
As it heals for 1-2 weeks, clots of mucus and crusts constantly form in the nose - this is also normal; doctor prescribes saline solutions to moisturize the nose and other medications to reduce swelling and speed up healing. Nasal breathing is fully restored gradually, usually by the 3rd week after surgery.