About Treatment
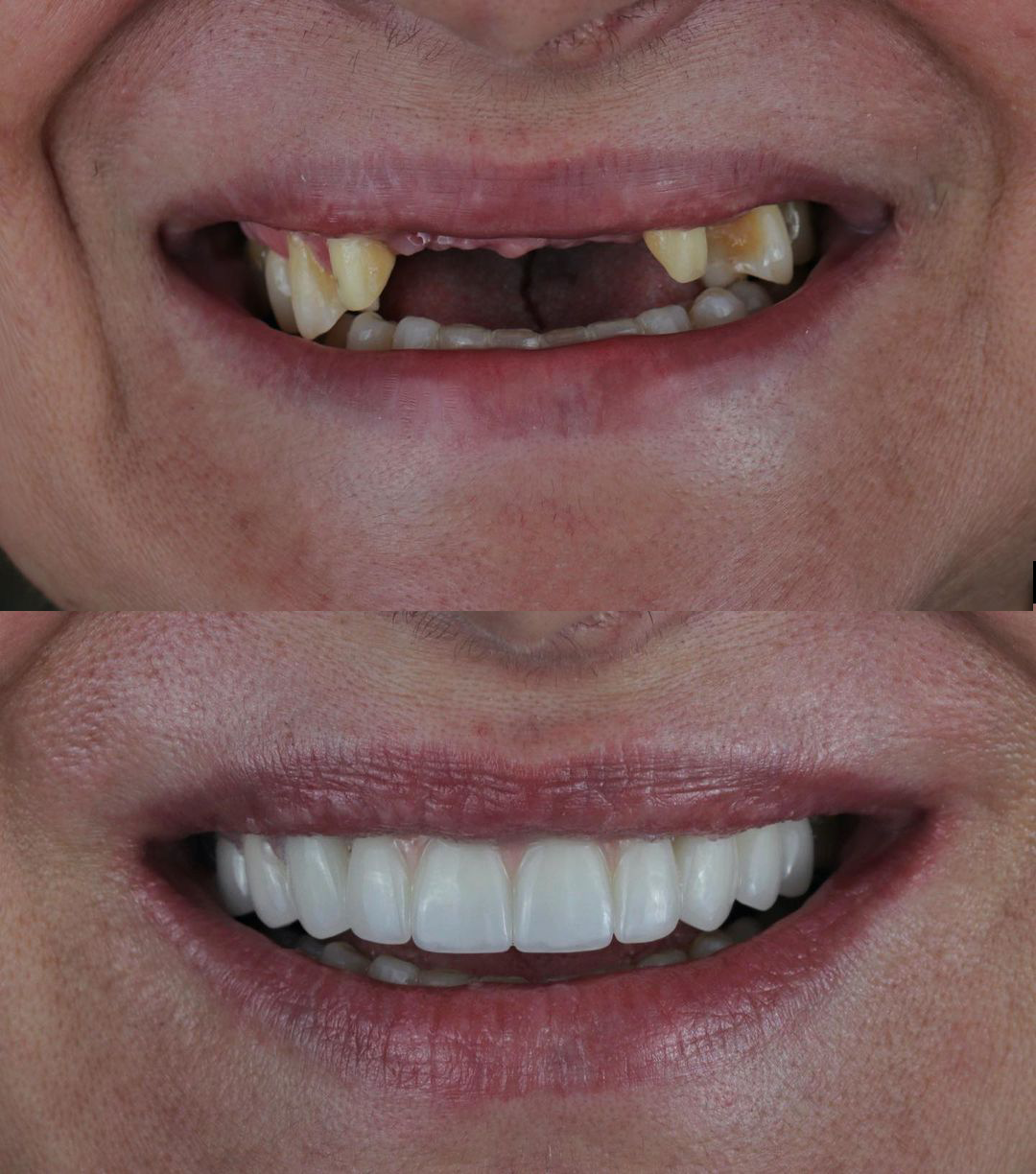
Dental implants are the best option to restore lost teeth once and for all.
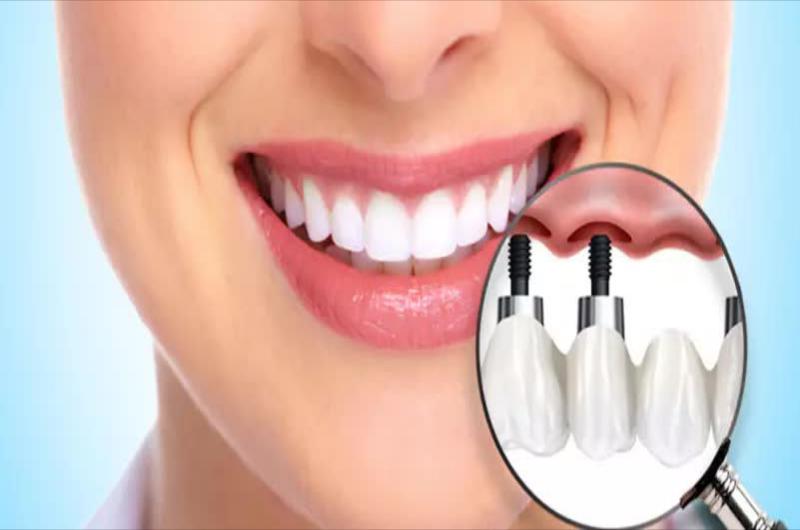
Today, implantation is the perfect method for restoring lost teeth. Only dental implants can restore the functionality of the tooth completely, including the root, without involving the adjacent teeth.
When are dental implants needed?
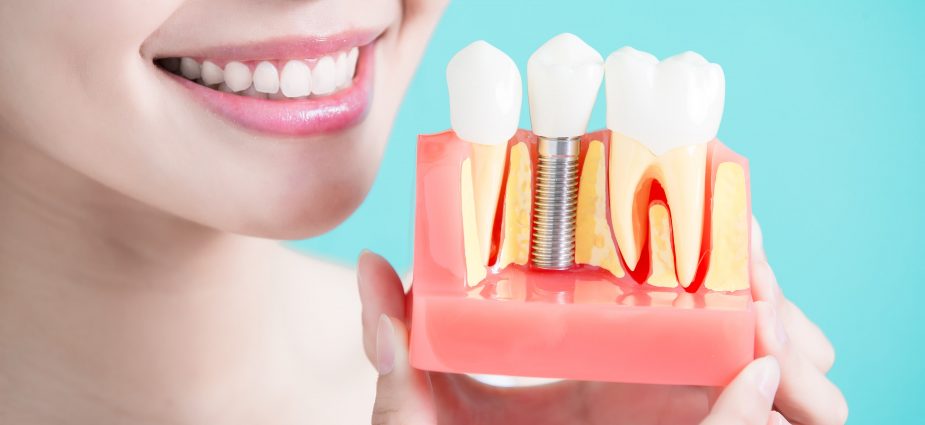
Dental implant is a metal post implanted in the jaw on which denture is attached. This method of attachment is much more reliable than the usual method, when structures are attached to adjacent teeth. In addition, this method avoids turning the adjacent teeth. Dental implants are also called intraosseous because they are implanted into the jawbone.
For some people, dental implants are the most comfortable way to restore lost teeth, for others - the only possible one. Conventional dentures and bridges are not suitable for those who suffer from diseases of the oral mucosa, have poorly expressed alveolar processes, and suffer from nausea while wearing conventional dentures.
Before applying dental implants, it is necessary to normalize the state of the oral cavity - to treat the teeth, get rid of bleeding gums. In addition, you should regularly visit your dentist and carefully follow your oral hygiene.
Dental implants usually last at least 10–20 years. The term depends on patient's care for the oral cavity, the state of health, the quality of the implantation performed and the place of the installed implant. So, implants replacing the front teeth experience less chewing load than implants in the area of the chewing teeth, and therefore last longer.
Dental implant is usually a multi-component design.
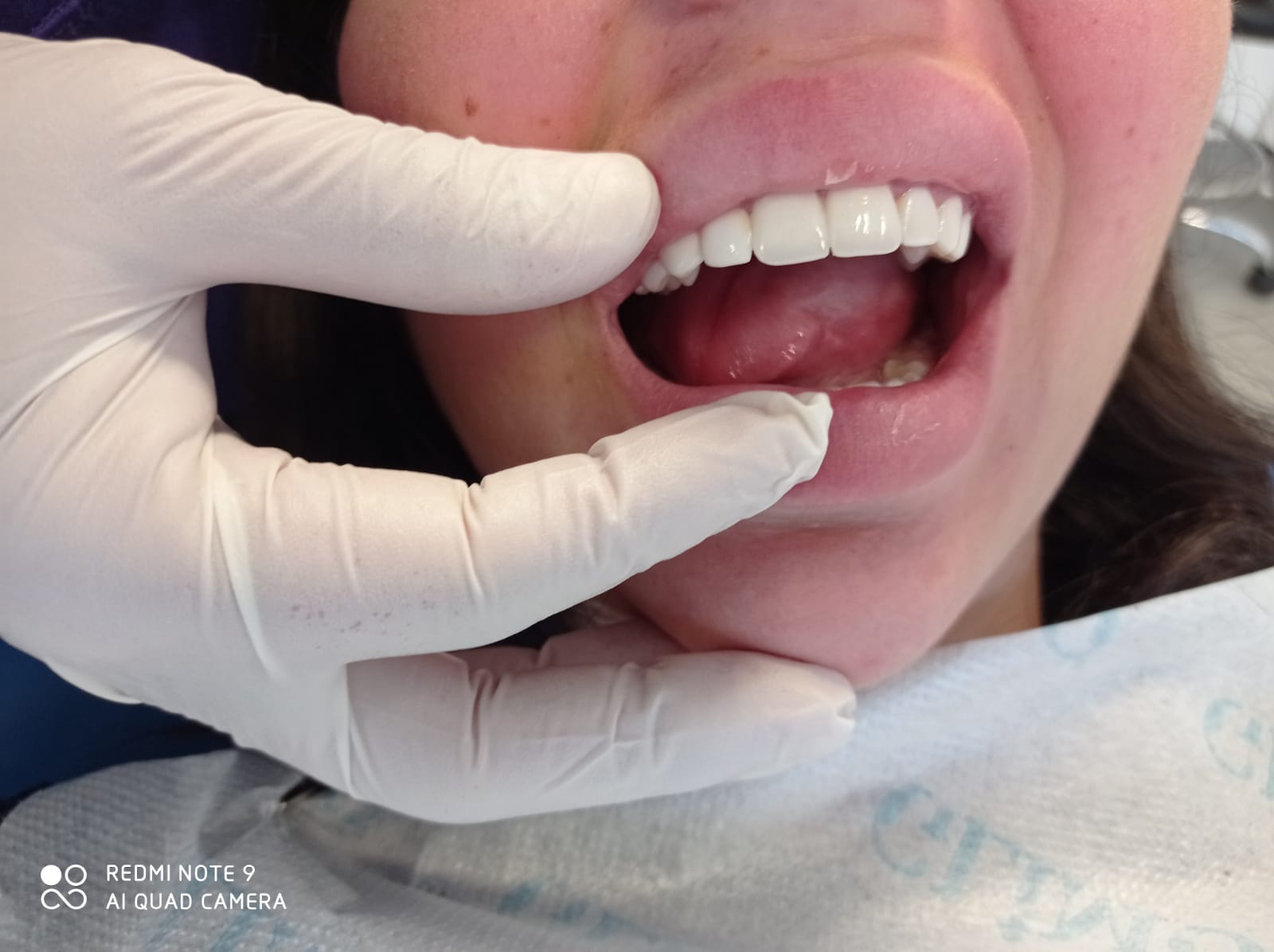
When prosthetic implant is performed, a titanium pin is first inserted into the tooth bone - it replaces the tooth root. In fact, this is a metal rod or screw.
The abutment serves as an intermediary between the implant and the crown of the tooth. This is the part of the entire structure that is visible above the gum. The denture attachment system can be screw, when the crown is connected to the abutment with a screw, or it can be cement. In this case, the two parts are securely connected with dental cement. The element material is metal, plastic (temporary option) or zirconium. The better and more durable the material, the more expensive it is. Crown is the part that is visible instead of the lost tooth. The crown can be made of various materials.
-
Indications
Loss of one or more teeth
Absence of several teeth in a row
If there are no last teeth in the row
If all the teeth are missing (complete adentia) -
Contraindications
age younger than 18–20 years
a number of diseases associated with blood clotting
serious diseases of the cardiovascular system
The body of dental implant is made of titanium or an alloy based on it. Why choose titanium? Firstly, this metal has the highest anti-corrosion properties. Secondly, it is a material that is biologically compatible with our body. Third, titanium has characteristics that are closest to bone tissue.
When choosing a dental implant, you need to pay attention to the shape of the product.
In modern dentistry, root-shaped implants are used. In fact, they follow the shape of a real tooth, which is considered the most functional. Sometimes, to install them, you have to increase the volume, and only then proceed to implantation.
Subperiosteal implants are installed in case of extreme thinning of the dentary bone. The structure is attached under the gum, between the bone and the periosteum (the tissue that surrounds the dental root). Subperiosteal implants occupy a large area, which allows them to hold the denture.
Endodontic stabilized implants are used if the tooth root is preserved. The structure is attached to the bone tissue through the apex of the root, which minimizes the healing time after implantation.
A special type of dental implants - intramucosal - are the only ones that are not installed in the bone tissue. They are used to stabilize lightweight or removable dentures.
As for crowns, the list of materials from which they are made today is very wide. However, not all of them are suitable for implants. Porcelain and solid ceramics, for example, are too brittle materials and can crack when interacting with a metal base. The most successful options are metal ceramics, ceramics on a gold base, metal-plastic (usually such crowns are used as temporary or provided that they are placed on implants immediately after their implantation), zirconium or aluminum dioxide. The last two options are the most aesthetic, durable and expensive. Their service life is at least 15–20 years.
Implants have obvious advantages over other restorative designs.
Advantages:
High biointegration. Titanium has interesting properties: if a rough screw made of this material is placed into the jawbone, after 2-4 months it will grow into it, and after another 1-2 months the screw will finally become firmly in the bone and will be ready for normal chewing loads.
Prevention of bone loss. The titanium root is a complete replacement for your own tooth root. It transfers the chewing load to the jawbone, creating physiological stimulation. This prevents bone loss.
Durability and strength of the structure. Breaking a titanium screw is much more difficult than breaking your own tooth. This is why an installed implant can last for decades.
Disadvantages:
Invasiveness. Dental surgery is required to place the screw into the bone. It is not traumatic, and after it they quickly recover, however, this is still more serious intervention than depulpation and turning, which are used when fixing crowns or bridges on own teeth.
There is a preparatory stage before implantation - during this period you undergo necessary examinations and prepare for the operation. After that, you should not have unhealed teeth and diseases of the oral cavity in the acute stage.
The next stage is the actual intervention. The doctor cuts and moves a small area of the gum and installs the implant.
Then the abutment is sequentially installed, and after complete healing - prosthesis itself.