About Treatment
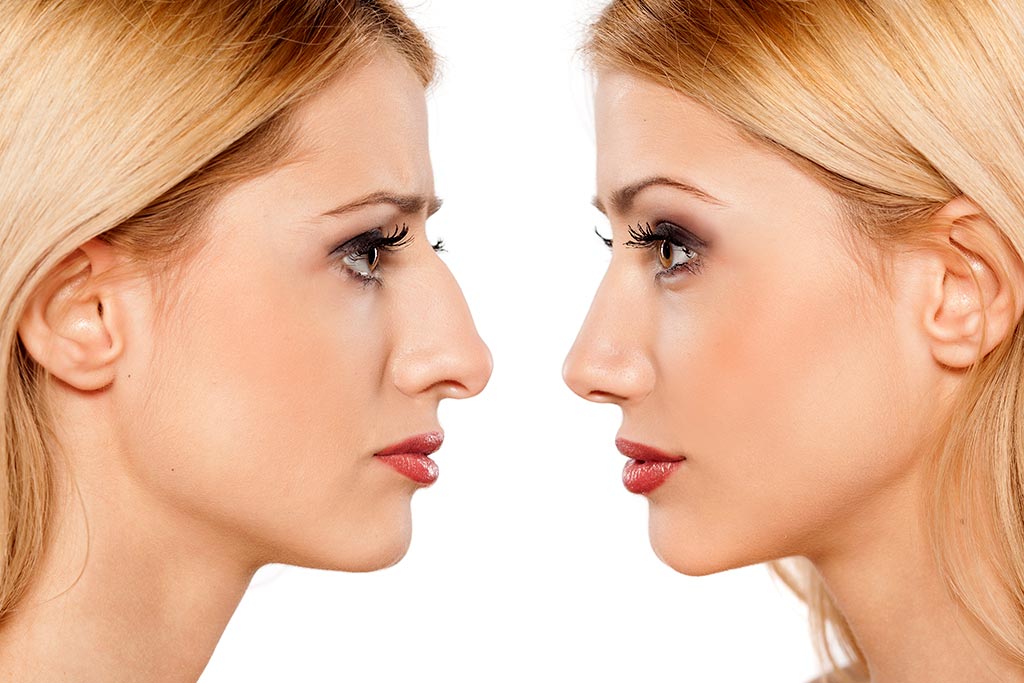
Rhinoplasty is a separate area of plastic surgery to correct congenital or acquired defects of the nose. With the help of rhinoplasty, it is possible to solve the problems of nasal breathing, to correct the external consequences of injuries, and also to correct the appearance for aesthetic reasons.
For many people who are unhappy with their own nose, rhinoplasty can be a lifesaver. However, this is a rather complex plastic surgery that requires great professionalism from the operating surgeon. Let's try to figure it out: what else is the specificity of such surgical interventions?
Should rhinoplasty be done?
Rhinoplasty can be recommended by a doctor in cases where congenital or post-traumatic deformities of the nose occur, and nasal breathing is impaired.
Aesthetic indications for rhinoplasty are:
saddle nose;
hump on the back of the nose;
hooked nose tip;
too pointed or thickened tip of the nose;
excessive length of the nose;
asymmetry of the wings of the nose;
dilated nostrils.
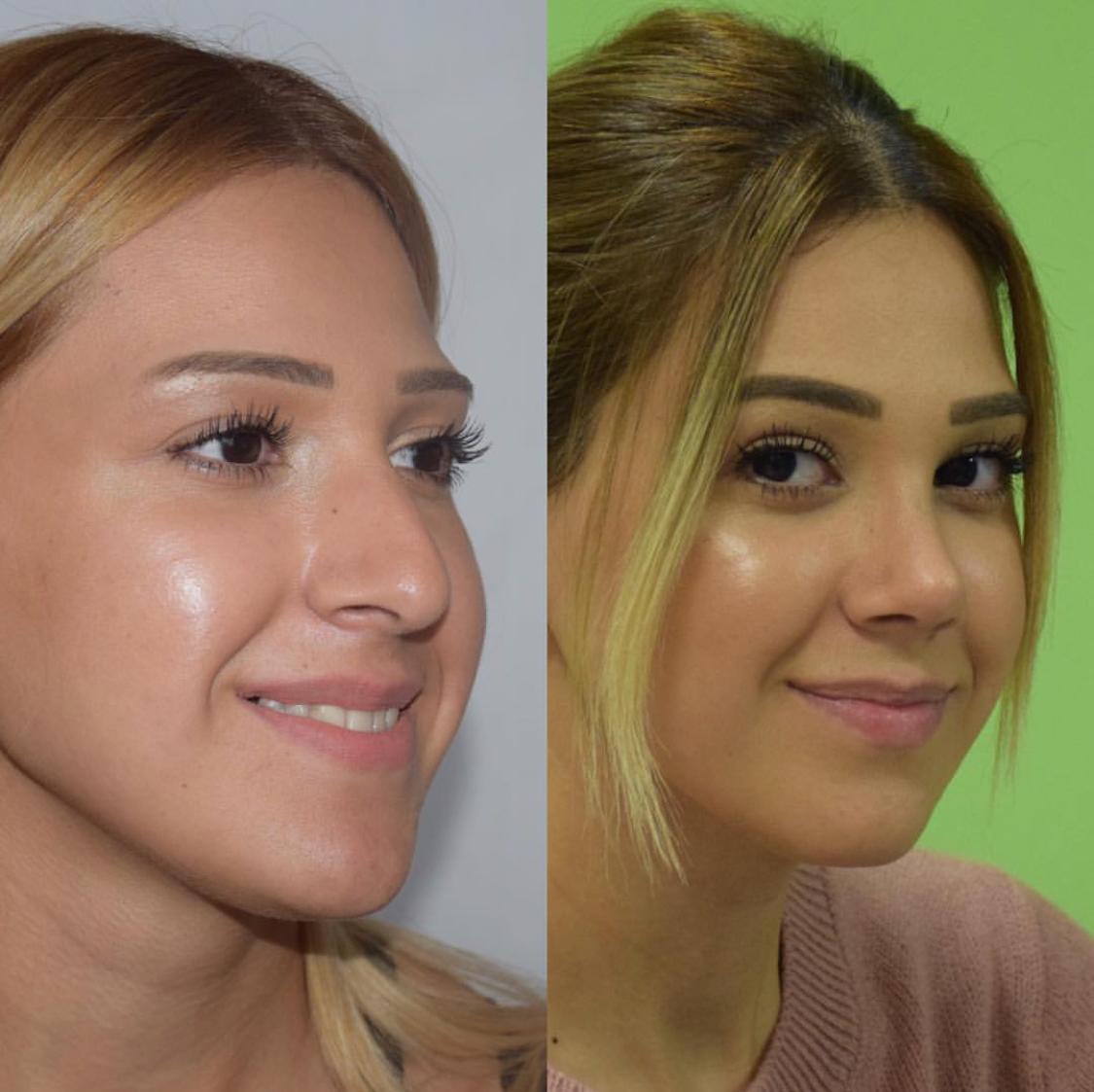

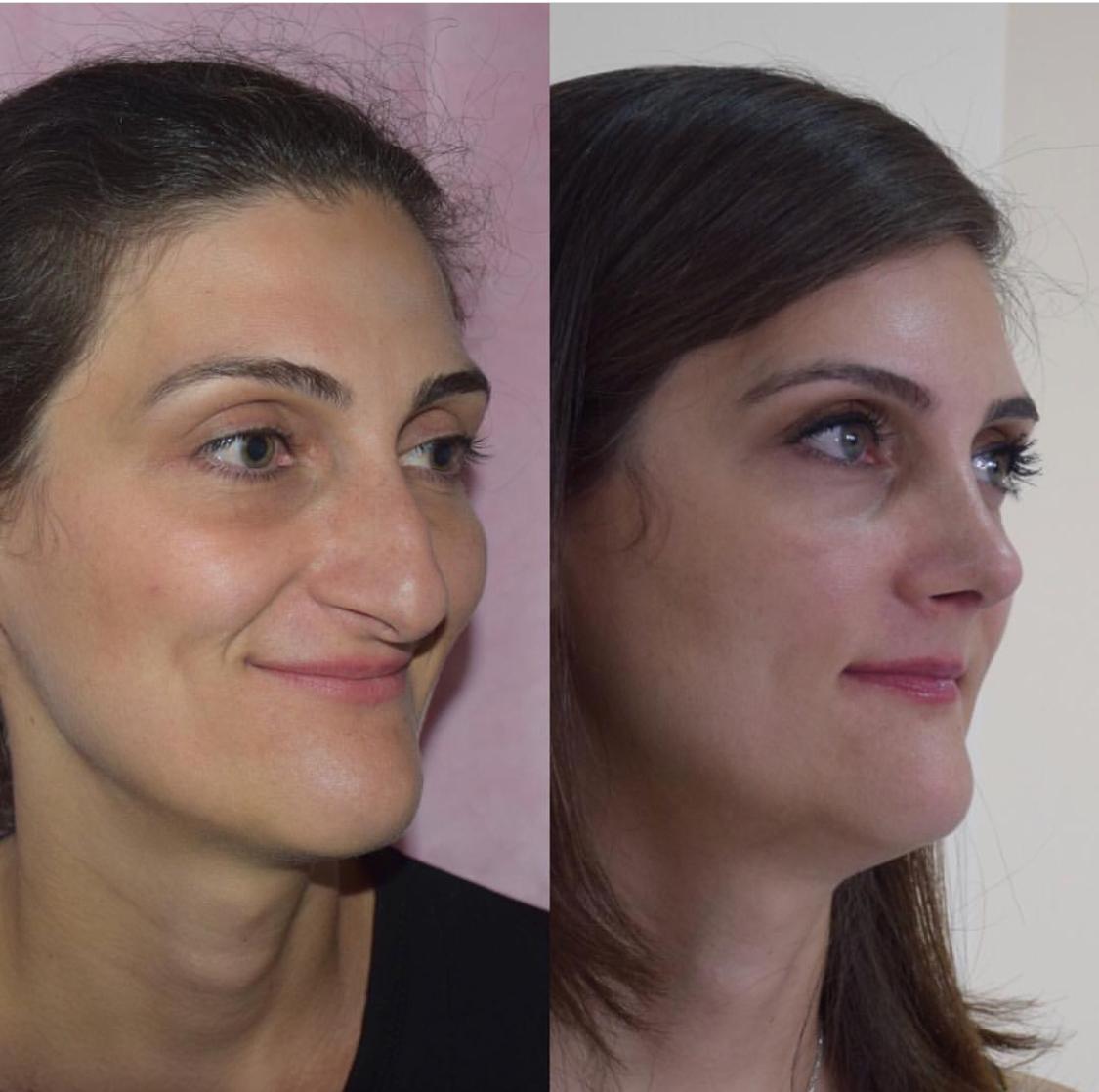
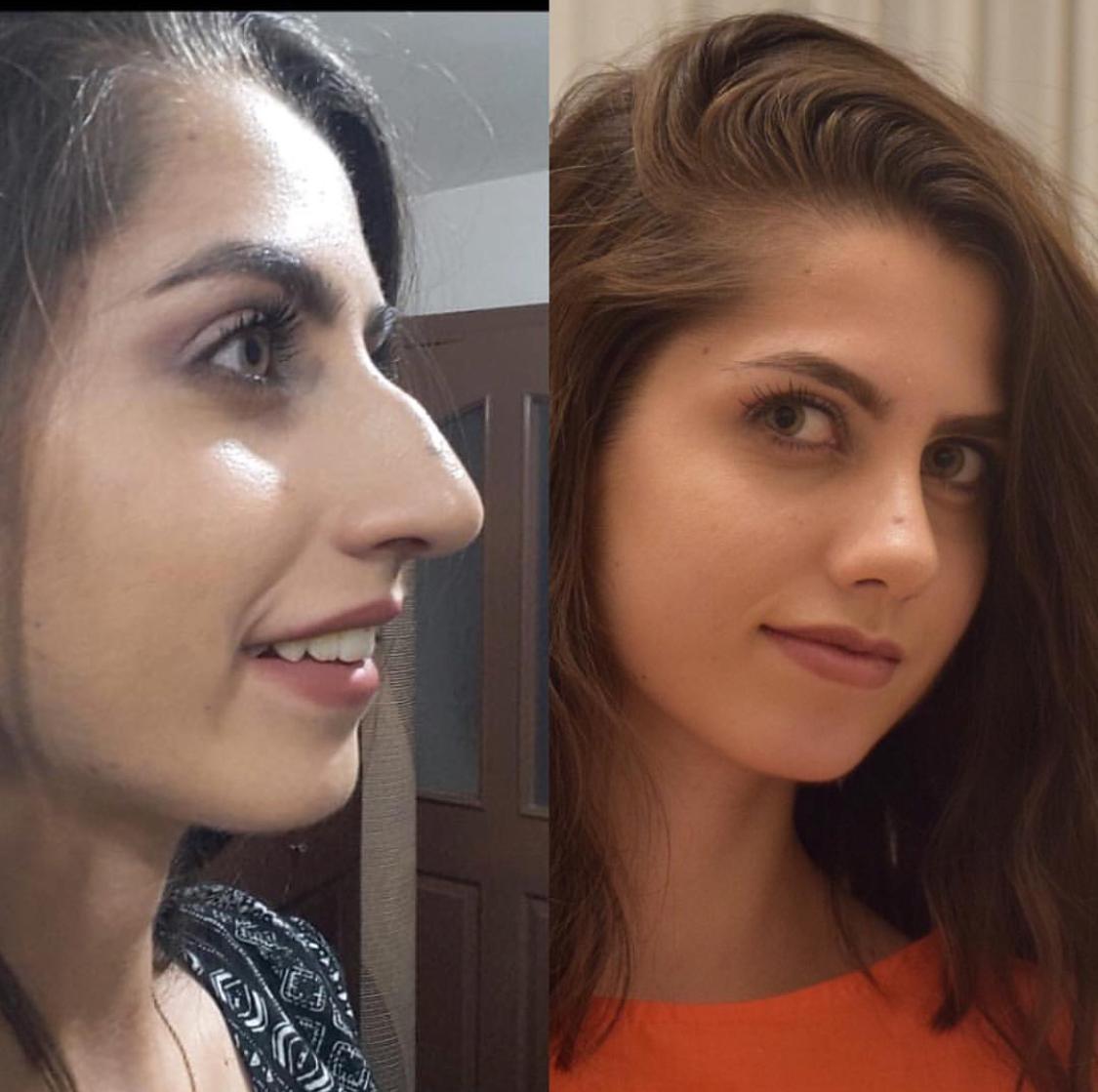
The presence of cosmetic defects of the nose is determined by the surgeon using special measurements, the results of which are compared with the average indicators. Patients with body dysmorphophobia (a mental disorder in which a person is overly concerned about a minor defect or feature of his body) should consult a psychologist.
For aesthetic indications, rhinoplasty is done only for adults, since at the time of the operation the body must be fully formed, and the patient is fully able to understand the essence of the operation and its possible consequences. Contraindications to rhinoplasty are: diseases of the cardiovascular system, liver and kidneys; diabetes; mental and oncological diseases; blood clotting disorder, systemic collagenosis. It is also not recommended to undergo surgery for people over 40 years old, whose ability to regenerate tissues is significantly reduced.

-
Operation Duration
1,5 - 3 hours
-
Rehabilitation Period
6 weeks
There are many types of rhinoplasty, each of which is designed to solve a specific problem and can affect different types of tissue.
Plastic surgery of the base of the nose is aimed at reducing the width of the nostrils. After surgery, subtle scars may remain at the base of the nose. The operation is performed both for aesthetic reasons and in order to reduce possible swelling of the nose after another operation in this area. Often, patients are representatives of the Negroid and Mongoloid races.
Plastic surgery of the tip of the nose. The most difficult type of rhinoplasty, capable of drastically changing patient's appearance, and requiring a great deal of experience from surgeon. Corrects hooked, upturned, axial displacement and other external defects of the tip of the nose.
Columella fix. Columella is the cutaneous part of the septum of the nose, in fact, it is the bridge between the nostrils. It may be too wide or too narrow, retracted or protruding. The defect can be corrected using prompt correction.
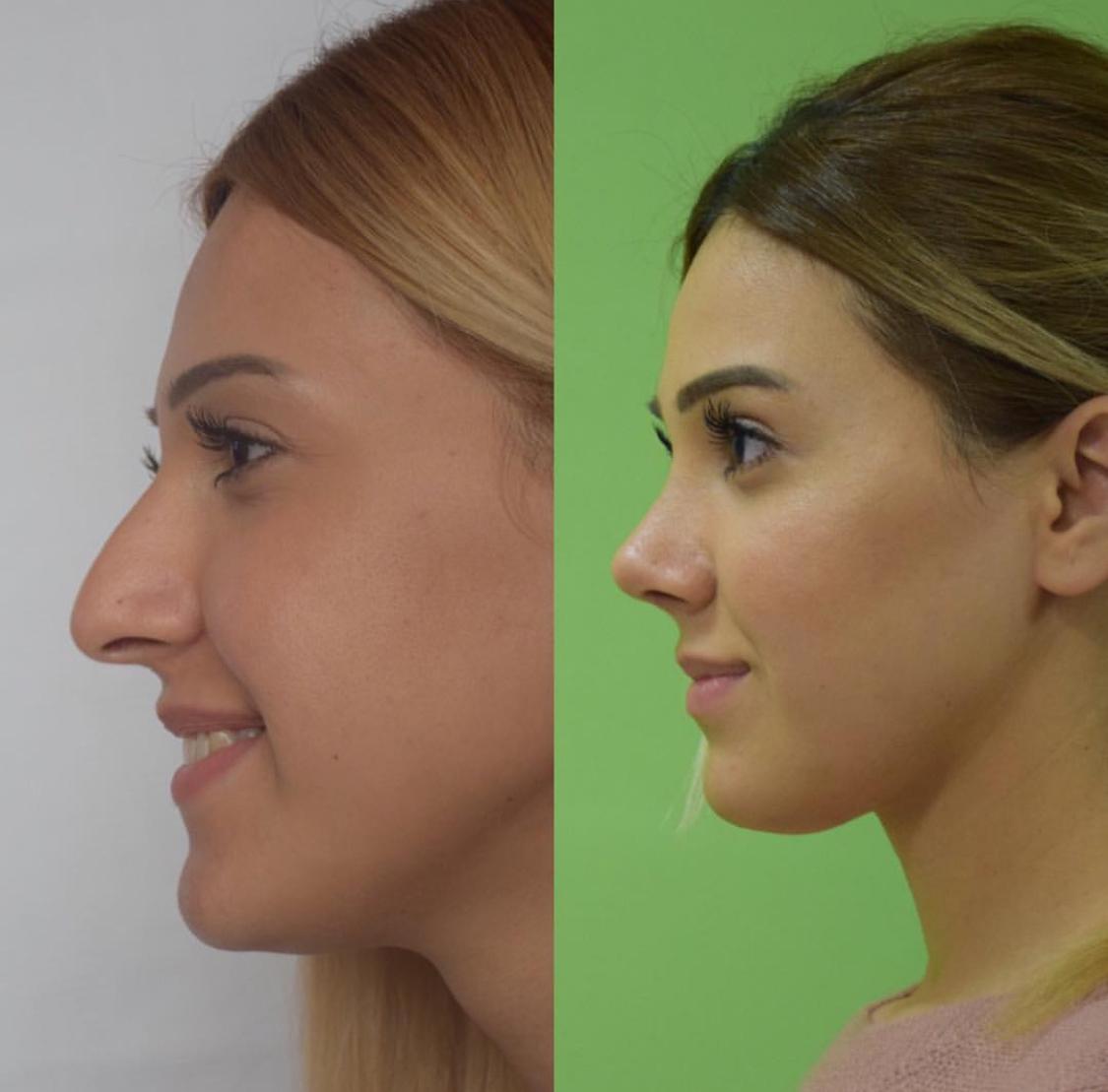
Correction of the shape of the nose. Giving the back of the nose the correct shape - smoothing the hump, aligning the axis. Affects bone and cartilage tissue.
Rinoseptoplasty. Correction of the curvature of the nasal septum in order to facilitate nasal breathing, solving the problem of snoring.
Augmentation rhinoplasty. This type of rhinoplasty is aimed at correcting defects in the nose by increasing the size of the nasal skeleton (usually used in cases of secondary rhinoplasty).
Grafting. Transplantation of the patient's own cartilage to create the desired shape of the nose. Cartilage tissue can be taken from the nasal septum, ear, or rib.
Reconstructive rhinoplasty. It is required for the restoration of defects in the nose after injuries, burns, as well as to correct the results of previous operations.
Conchotomy (including laser). Partial or complete removal of the hypertrophied mucous membrane of the turbinates in case of problems with nasal breathing.
Electrocoagulation. Sparing effect of electric current on the nasal mucosa in cases of slight hypertrophy of the turbinates.
Laser rhinoplasty. A laser is used as a tool instead of a scalpel, which makes the operation less traumatic.
Non-surgical rhinoplasty. Modeling the shape of the nose using dense gels - fillers.
Nose contouring. A non-surgical method of correcting small external defects of the nose through injections of hyaluronic acid.
Rhinoplasty with hyaluronic acid injections and fillers belongs to the field of cosmetology, not surgery, and has a minimal rehabilitation period. Surgical methods leave behind mild swelling of the nose and the area around the eyes, which subside at the time the cast is removed on the seventh day. A plaster cast may be required for up to ten days. After the operation, special silicone splints are inserted into the sinuses, which are removed after a day. This approach allows the patient to breathe through the nose right after the surgery. The course of rehabilitation depends significantly on the age of the patient and the individual characteristics of his body. After the splints are removed and the cast is removed, you will need to visit your doctor periodically to monitor healing. Physical activity, swimming, and wearing glasses for the first three weeks after surgery are not recommended. Foods that are too cold or hot should be avoided so as not to provoke nosebleeds in the first three days. When planning a nose job, it is best to take a vacation for at least half a month.
In aesthetic surgery, rhinoplasty is considered one of the most difficult areas. In order for it to be successful, a thorough examination and computer modeling of the future shape of the nose are first carried out. Sparing techniques are used to facilitate the rehabilitation period. Nevertheless, after rhinoplasty, a number of complications are possible, which appear both in the early postoperative period and later.
Unsatisfactory healing is evidenced by inflammatory processes in the operated tissues, the formation of hematomas, nosebleeds, thinning of the nasal skin and discoloration. In the long-term period, dry crusts in the nasal cavity can occur, which is fraught with a decrease in smell and difficulty in nasal breathing.
So, the results of rhinoplasty can be judged only a year after the operation. If there is a need for re-correction, then it can be carried out no earlier than six months to a year after the primary surgical intervention. But by contacting an experienced surgeon who specializes in this particular type of plastic, you will reduce the risk of possible complications to a minimum.