About Treatment
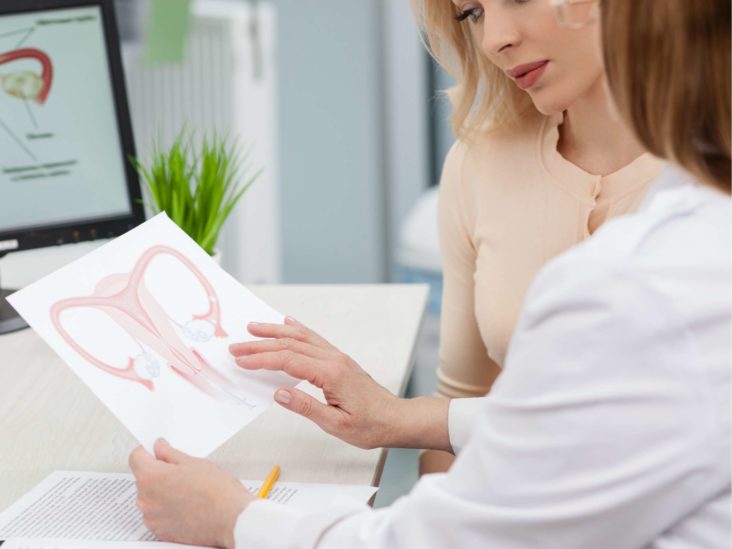
Hydrosalpinx is a pathological condition characterized by an excessive accumulation of secretion in the cavity of the tube, arising from the impossibility of its outflow due to blockage of the lumen of the tube. The tube becomes impassable in a certain area due to circulatory and lymphatic flow disorders that occur against the background of acute salpingitis (inflammation of the fallopian tube) and provoking the formation of adhesions in the fallopian tube.
A simple hydrosalpinx is distinguished if one closed cavity or follicular arises in the tube when the lumen of the pipe is divided into several cavities. After the formation of cavities, a transudate begins to accumulate in them (the secret of the fallopian tube), the wall of the tube stretches (reaching a few centimeters in diameter). Periodically, the resolution of the process is possible: the fluid through the uterus is poured out or absorbed by the wall of the tube, but due to the presence of adhesions, after some time, the hydrosalpinx occurs again. Therefore, a chronic relapsing course is characteristic of the disease. Hydrosalpinx typically occurs on both fallopian tubes.
Complaints arise with an outflow of transudate: cramping pains in the pelvic region may appear, accompanied by abundant outflow of fluid from the vagina. The liquid is transparent, may have a yellowish tint. More often, a woman simply notes periodic or constant watery discharge from the genital tract (when emptying the hydrosalpinx into the uterus and vagina). When the pipe ruptures, a picture of an acute abdomen occurs, when suppurating the fluid, weakness, intoxication, and an increase in body temperature (pains may be absent, since the sensitivity in the overgrown walls of the tube).
Diagnostics
During an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs, the presence of a smooth-walled one or two-sided tumor-like formation in the area of the uterus is diagnosed. Diagnostic laparoscopy is performed to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment
Treatment - surgical, reconstructive-plastic operations are performed by laparoscopic access, using endovideo surgical complexes that allow to most effectively restore the patency of the fallopian tube. In the postoperative period, a course of physiotherapy is prescribed to prevent the development of adhesions. The fallopian tube can be removed by rupture or suppuration (transudate is a breeding ground for bacteria), in the absence of a woman's desire to maintain the ability to have a baby. Immediately after the operation, a course of restorative physiotherapy is carried out to prevent the formation of adhesions.
The sooner a pathology is discovered and treatment is started, the more chances there are for a favorable result. In the acute period, surgery is not performed. First, drug therapy is prescribed to eliminate the inflammatory process, and only after that the day of surgery is selected.
Is it possible to treat without surgery?
It is almost impossible to do without surgical treatment in hydrosalpinx. When performing operation, doctors adhere to organ-preserving techniques. The age of patient, the presence of her children and the desire to realize reproductive function in the future are taken into account.
With hydrosalpinx, laparoscopy is usually performed - a gentle method for removing a pathological site. Access to the abdominal cavity is through three small punctures. If the abscess ruptures, open surgery may be required.
-
Causes
Inflammation of the appendages;
After surgery in the abdominal cavity;
As a result of internal bleeding;
Due to endometriosis;
Tumor in the pelvis.
-
Symptoms
Production of serous fluid in the tube;
Significant increase in temperature (up to 40 degrees);
Weakness, sweating;
Pain in the lower abdomen and in the inguinal areas;
Cardiopalmus.
-
Complications of Disease
Infirtilite;
Pipe rupture;
Chronic infections of the female genital organs;
Early cancer.
The main reason for the formation of hydrosalpinx is the narrowing of the lumen of the fallopian tube from two sides, adhesions in the oviducts may appear:
with inflammation of the appendages;
after surgery in the abdominal cavity;
as a result of internal bleeding;
due to endometriosis;
with a tumor in the pelvis.
The risk of adhesive disease and, as a consequence, the formation of a hydrosalpinx increases with the early onset of intimate life, neglect of contraception, non-observance of personal hygiene, abortion, hormonal imbalance and self-administration of oral contraceptives (without doctor's recommendation).
In the earliest stages of fluid formation in the fallopian tube, symptoms may not be present in women. Over time, characteristic signs appear.
Symptoms and signs:
pain on one or both sides in the lower segment of the abdominal cavity;
discomfort during intimacy;
copious watery discharge from the genital tract;
increase in body temperature (with inflammation);
infertility.
The main danger of hydrosalpinx is that the amount of fluid in the cavity of the fallopian tube gradually increases. The culmination of the pathology may affect the integrity of the walls of the oviduct and internal bleeding. In addition, with hydrosalpinx, the risk of inflammation increases significantly. Transudate is a breeding ground for microorganisms. Therefore, infection begins to develop in the fluid. With this combination of circumstances, hydrosalpinx is complicated by adnexitis.
With hydrosalpinx, the patency of the oviducts is usually impaired. They completely or partially lose their function. With hydrosalpinx, it is almost impossible to get pregnant. Often this problem causes primary or secondary infertility. If a woman succeeds in becoming pregnant with fluid in the tube, then there is a high risk of an ectopic pregnancy. If the pregnancy is still normal, then baby is likely to have problems due to intrauterine infection.
Surgical treatment is aimed at removing the pathological section of the fallopian tube. If the hydrosalpinx is large, you have to remove the pathological zone.
Modern surgery in gynecology allows simultaneously with the removal of the pathological area to perform plastic surgery of the tube, if necessary (woman plans to give birth in future). But some situations do not allow you to save the function of the appendages, and the tubes are removed as a whole.
After surgery, patient is prescribed restorative therapy. It is required to normalize the hormonal background, increase immunity, get rid of inflammation of the appendages and prevent the appearance of the hydrosalpinx (with the tubes preserved) in future.
It is believed that hydrosalpinx and pregnancy are incompatible concepts. Indeed, with such a problem, it is difficult to become pregnant naturally, and if it occurs, then there is a high risk of complications. However, after treatment, a woman has a chance to give birth on her own. In this case, conception can happen even after removal of the fallopian tubes.