About Treatment
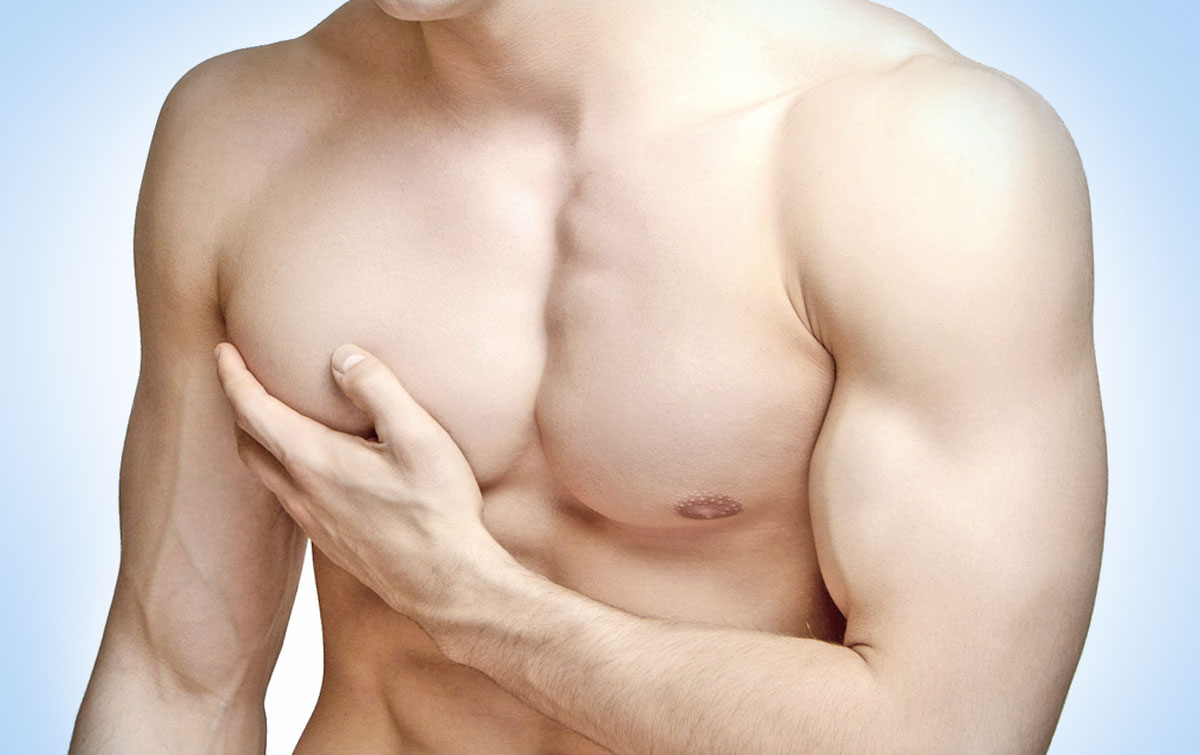
Gynecomastia - enlargement of the male breast - is a problem that not only causes immense discomfort in patients, but also often leads to impaired social adaptation. A man who has severe gynecomastia feels uncomfortable in fitness club, sauna, on the beach, and may experience problems in his personal life. Because of false shyness, he often avoids going to a doctor, although gynecomastia requires professional treatment.
There are two types of gynecomastia in men - true, caused by abnormal growth of glandular tissue in the "female type", and false - when breast augmentation occurs due to local deposition of fat. Against the background of general obesity, both types of gynecomastia are often manifested.
The cause of true gynecomastia can be a number of factors: hormonal imbalance, taking certain medications, impaired liver function and metabolism. Recently, however, breast growth has been observed in healthy young men who are actively involved in sports. Gynecomastia here occurs due to the uncontrolled use of anabolic steroids, which are widely used to build muscle mass.
The initial treatment for gynecomastia is carried out by endocrinologists and mammologists. If gynecomastia is caused by adolescent hormonal imbalances, it often goes away on its own. But if conservative treatment does not work, patients over 18 years of age are advised to consult a surgeon: gynecomastia that occurs in men of reproductive age is considered a direct indication for surgery.
A prerequisite for performing an operation to treat gynecomastia is a consultation with a mammologist oncologist. Surgical treatment of gynecomastia is a simple, standard procedure. If the problem is caused by the growth of glandular tissue, it is excised through small incisions. When gynecomastia is also accompanied by excessive stretching of the skin, it may be necessary to tighten it, and sometimes transfer the nipple to its original level: incisions are made in the areola and after healing they will be hardly noticeable. With false gynecomastia, provoked by obesity, liposuction is used - removal of local fat deposits, and, if necessary, excision of excess stretched skin.
After the gynecomastia is removed with the help of a surgical operation, patient goes home a day later, after a week he can return to normal life with minor restrictions: for about 4 weeks, you need to wear a fixing bandage, avoid physical exertion, and visit sauna.
Why is it dangerous if you don't treat the disease?
Lack of treatment or low efficiency of conservative therapy leads to the long-term existence of pathology. In the course of its development, the risk of the disease degenerating into cancer increases.
Usually, the first changes are amenable to drug treatment. However, there is no more than 4 months to take action. Therefore, you should immediately consult a doctor at the first symptoms in order to get rid of gynecomastia both without surgery and without consequences.
Treatment methods
Gynecomastia of physiological types does not require specialized treatment in men; it passes without surgery and medication.
Drug therapy involves the use of hormonal drugs. If there is no improvement against their background, plastic surgery is performed:
mastectomy combined with liposuction;
mastectomy, preserving the contour of the areola;
endoscopic mastectomy.
Removal of breast tissue is performed from the para-areolar approach, i.e. through a small incision less than 4 cm in the areola of the nipple. It is possible to carry out a combined operation when liposuction is additionally performed to remove adipose tissue.
The choice of a specific method of the operation is carried out by doctor, taking into account the medical indications, the individual characteristics of the patient and his wishes. Plastic surgery is performed at the same time, which provides an excellent aesthetic effect from the operation. Thanks to modern equipment and high qualifications of our oncosurgeons and plastic surgeons, surgical treatment of gynecomastia is carried out on an outpatient basis within one day.
After the operation, patient spends the day in a comfortable hospital ward under the supervision of a doctor, and in the evening he returns home. Upon discharge from the clinic, the doctor gives detailed recommendations about the postoperative period (wearing compression hosiery, limiting physical activity, etc.).
-
Procedure Duration
1-2 hours
-
Recovery Period
1-2 weeks
Gynecomastia, first of all, occurs as a result of a decrease in testosterone in hypogonadism (insufficiency of the function of the gonads) and in hormonally active tumors of the adrenal cortex and testicles. With gynecomastia, there is a feeling of heaviness, distention and discomfort in the breast area. When probing, a densely elastic mobile formation with clear contours is determined, painless.
Gynecomastia in the neonatal period: boys are born with enlarged mammary glands, this condition persists for 2-4 weeks, then the mammary glands shrink
Gynecomastia during puberty (12 to 15 years): This increase normally lasts no more than two years
Gynecomastia in old age (over 45 years old): the mammary glands enlarge due to age-related increases in estrogen in the body
Other reasons:
increased release of prolactin;
disturbed metabolic processes;
cardiovascular insufficiency;
local injuries;
HIV;
intoxication of the body;
renal failure;
cirrhosis;
taking certain medications;
alcoholism, drug addiction.
With the true type of gynecomastia, the stroma and glandular tissue grow abnormally. It is divided into three types:
in children under one year old and newborns, which are characterized by an increase in the mammary glands in 60-90% of cases due to the ingestion of maternal hormones into the body while still in the womb;
adolescent (30-60% of cases), predominantly arising at 13-14 years of age in the form of a bilateral increase due to hormonal immaturity;
in the elderly, associated with hormonal changes.
With the false type of gynecomastia, there is an active deposition of fat in the area of the mammary glands.
Doctor examines patient, palpates the testicles and mammary glands, takes anamnesis. Tests are then done for hormonal testing. This is a blood test for FSH, estradol, hCG, testosterone, prolactin, LH, etc. To exclude tumors, CT, X-ray, ultrasound of the scrotum are prescribed. If cancer is suspected, an ultrasound scan, biopsy is performed.
The following symptoms are characteristic:
increase in mammary glands up to 15 cm in size and weight - up to 150 g;
increase in the areola (up to 3 cm), nipple, increased pigmentation, milky discharge (rarely);
sensitivity of the nipples against the background of painless breasts;
feeling of pressure, distention of the mammary glands