About Treatment
Today, radiation is considered one of the 3 main ways to fight cancer, as well as surgery and chemotherapy.
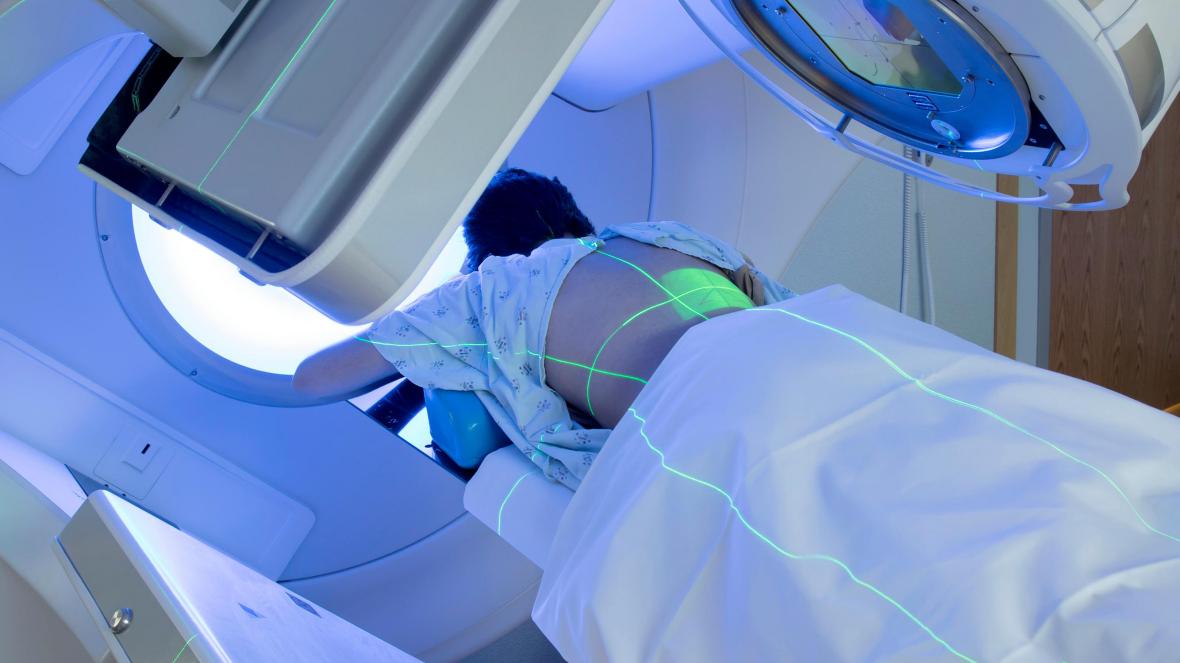
Radiation Oncology is a branch of medical science that is devoted to the study of the effect of ionizing radiation on various oncological diseases. Without going into details - this method consists in the following: radiation is directed to the site of an organ affected by a tumor formation in order to remove malignant cells, while it is necessary to minimize the damaging effect on healthy cells and tissues.
In order to deal with the issue of radiation, it is necessary to begin to understand the variety of types of radiation that exist today. The most common type of radiation is remote radiation. In 1950, cobalt therapy was invented and actively applied, which served as the beginning of the first waves in the field of radiation. Another important invention is a linear accelerator. At present, radiation technology can no longer be imagined without modern computer technologies, as well as methods for modeling rays.
The following types of remote radiation are distinguished, which can significantly increase the effectiveness of therapy by increasing the accuracy of the effect of radiation on tumors:
1.3D-conformal radiation therapy
2. Radiotherapy with the ability to modulate the intensity of rays
3. Stereotactic radiosurgery, the effect of which is to use a narrowly focused rays.
4. Technologies that combine the use of 3D and 4D modeling technologies, as well as modulation of ray intensity.
Radiotherapy
Today, it is one of the most common ways to treat cancer. In general, radiation oncology initially developed in this direction, although it has undergone significant changes over time. Radiation therapeutic effect involves the use of wide rays that have an ionizing effect. Normally, radiation therapy should take place in several sessions. Recommended for use in the presence of many types of tumors, either as the only method of treatment, or in combination with some others.
Radiotherapy preserves the anatomy and function of the organ, improves the quality of life and survival rates, reduces pain. For decades, radiation therapy for cancer has been widely used in most oncological diseases. No other cancer treatment is capable of substituting an equally effective RT for the purpose of killing a tumor or alleviating pain and other symptoms.
Radiation therapy is used in the treatment of almost all malignant neoplasms, no matter in which tissues and organs they arise. It is used alone or in combination with other methods, such as surgery or chemotherapy. Radiotherapy can be carried out in order to completely cure cancer or relieve its symptoms when the removal of tumor is impossible.
Currently, a complete cure is possible in more than 50% of cases of malignant tumors, for which radiotherapy is extremely important. Radiation therapy in oncology involves the treatment of malignant neoplasms using high-energy radiation. The oncologist-radiologist uses radiation to completely cure cancer or to alleviate pain and other symptoms that are caused by the tumor. Radiotherapy damages cancer cells by adversely affecting their DNA, making the cells no longer able to divide and grow. This cancer treatment is most effective in killing actively dividing cells.
The high sensitivity of cancer cells to radiation is due to two main factors:
-they divide much faster than healthy cells and
-they are not capable of the same effective repair of damage as healthy cells.
Brachytherapy - Internal Radiation Therapy
Radiation in cancer is also possible with the help of radiation sources that are placed in patient's body (brachytherapy, or internal radiotherapy). In this case, the radioactive substance is located inside the needles, catheters, grains or special conductors that are temporarily or permanently implanted inside the tumor or placed in the immediate vicinity of it.
Brachytherapy is a very common method of radiation therapy for cancer of the prostate, uterus and cervix or breast. The radiation method so accurately affects the tumor from the inside that the consequences (complications after radiation therapy to healthy organs) are practically eliminated. For some patients with a malignant tumor, radiotherapy is prescribed instead of surgery. In this way, prostate cancer and laryngeal cancer are often treated.
Adjuvant Radiotherapy
In some cases, RT is only part of patient's treatment plan. In those cases when radiation treatment for cancer is prescribed after surgery, it is called adjuvant. For example, a woman may receive radiation therapy after organ-preserving surgery on the mammary gland. This allows you to completely cure breast cancer and preserve the anatomy of the breast.
Induction Radiotherapy
In addition, it is possible to conduct radiotherapy before surgery. In this case, it is called neoadjuvant or induction and can improve survival rates or make surgery easier for surgeon. Examples of this approach are irradiation in cancer of the esophagus, rectum or lung.
Combined Treatment
In some cases, before surgical removal of cancer, RT is prescribed to patient together with chemotherapy. Combined treatment can reduce the amount of surgical intervention that might otherwise be required. For example, some patients suffering from bladder cancer, while prescribing all three methods of treatment, manage to completely preserve this organ. It is possible to simultaneously conduct chemotherapy and radiotherapy without surgery to improve the local response of the tumor to treatment and reduce the severity of metastasis (tumor spread).
In some cases, for example, with cancer of the lungs, organs of the head and neck or cervix, such a treatment may be quite sufficient without the need for surgery.
Since radiation damages healthy cells, it is very important that it is aimed at the area of the cancerous tumor. The less radiation affects healthy organs, the less the negative consequences of radiation therapy are possible. That is why, when planning treatment, various imaging methods are used (imaging of the tumor and its surrounding organs), which ensures accurate delivery of radiation to the tumor, protection of adjacent healthy tissues and a decrease in the severity of side effects and complications of radiotherapy subsequently.
In addition to the method of active cancer treatment, radiotherapy is also a palliative method. This means that RT can alleviate the pain and suffering of patients with progressive forms of malignant neoplasms. Palliative radiation treatment for cancer improves the quality of life of patients experiencing severe pain, difficulty in moving or eating with a growing tumor.
-
Types of Radiotherapy
Proton radiation therapy
Ion radiation therapy
Electron beam therapy
Gamma therapy
X-ray therapy
-
Recommendations
Giving up bad habits, such as smoking, drinking alcohol
Eating high-calorie foods
Drinking more water
Do not wear synthetics
Avoid direct sunlight
-
Treatment Duration
The duration of the course of radiation treatment and dose are directly dependent on the type of disease. The term of treatment with intracavitary irradiation lasts much less. It may consist of fewer procedures and rarely lasts more than four days.
Indications for radiation therapy:
Treatment of malignant diseases
- undifferentiated tumors are more sensitive to radiation than differentiated forms
- in inoperable forms of cancer, the symptoms are controlled by radiotherapy
In radiotherapy for the treatment of tumors in the maxillofacial area, it is mandatory to pre-rehabilitate patient's oral cavity - removal of gangrenous roots, teeth, which are a source of focal infections, teeth with periapical changes. Healthy areas around the irradiation field are protected by lead shields.
Side effects depend on the applied dose and general condition of the body:
Fatigue and exhaustion
Skin reactions in the treated areas - rash, redness
Loss of appetite
Decreased immunity - decreased number of white blood cells
Hair loss
In the treatment of tumors of the genitals and pelvic area, radiotherapy can lead to infertility.
To strengthen the effectiveness of radiation therapy and minimize side effects of rays on the body, as well as recover quickly and eliminate unpleasant consequences, compliance with the rules and following medical recommendations will help: After each session, rest is required for at least 4-5 hours. Nutrition must be filled with a sufficient amount of healthy vitamins and minerals. Food and dishes should be easily absorbed by the body, since organs after therapy are significantly weakened. You should eat in small portions several times a day and drink sufficient amount of liquid. For a full and final release of toxic elements and to remove radiation from the body, at least 2-2.5 liters should be consumed per day.
Underwear should be made of natural materials. Clothing should let air through, allowing the body to "breathe." Strictly observe the rules of hygiene. Every day you need to devote time to the hygienic component of life. It is recommended to wash with warm, non-hot water using a mild soap without unnecessary chemical additives. It is better to discard the washcloth and sponge while washing the body. For the entire course of therapy it is forbidden to use perfumes. A place exposed to radiation requires protection from direct sunlight. Ultraviolet rays are detrimental to the condition of weak skin. Every day, patients do breathing exercises. Exercise saturates the tissues and cells of organs with oxygen. Use gel toothpaste, soft brush. Often walk in the fresh air with short walks for at least 2-3 hours every morning and evening. Refuse alcohol-containing drinks and tobacco products.