About Treatment
In the past, the possibilities of rendering assistance to people with profound hearing loss (IV degree) and absolute deafness were limited, since in such cases hearing aids are practically ineffective. The active introduction of cochlear implantation (implantation of a unique device - a cochlear implant into patient's inner ear) in recent years has given such patients a real chance of effective rehabilitation and return to an active lifestyle. At the moment, the cochlear implantation system is the most perfect device for helping people who cannot reach the world of sounds. Cochlear implantation has been successfully performed worldwide for about 30 years.
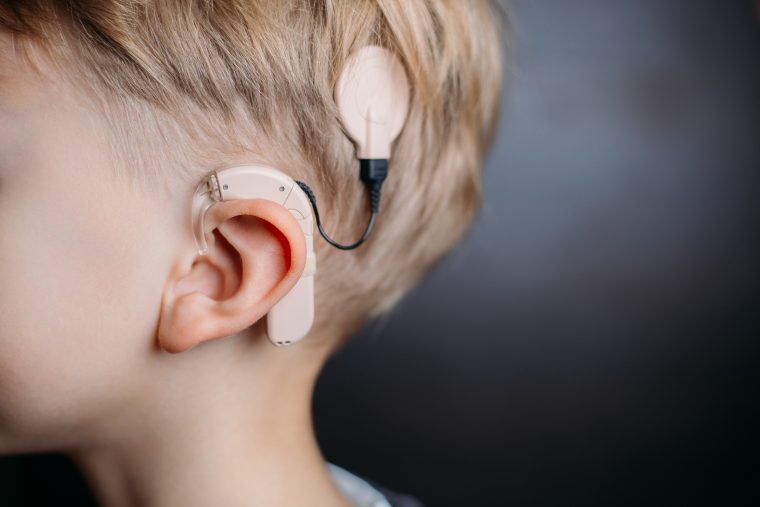
Cochlear implantation system is an electronic device that acts as damaged or missing hair cells by providing electrical stimulation to intact nerve fibers. Cochlear implantation system is a high-tech product, a device that enables people to hear in case of bilateral sensorineural hearing loss of grade IV and more. This means that a person with a cochlear implant will be able to communicate with their family, friends, colleagues.
Cochlear implant system has two components:
The first component of the cochlear implant system is a cochlear implant.
It delivers sound information in the form of electrical impulses directly to the fibers of the cochlear nerve, by passing the damaged receptor apparatus of the inner ear. The implant consists of a receiver / stimulator and an electrode array. The receiver / stimulator is a small circular plate that sits under the skin behind the ear and receives signals, transforming them into electrical impulses. The electrode grid is a thin thread that emerges from the receiver / stimulator and is located in the inner ear in close proximity to the fibers of the cochlear nerve. The electrode grid consists of platinum electrodes, and through them electrical impulses enter the cochlear nerve.
The second component is the speech processor.
This is a small computer. The speech processor can be pocket-sized (in the form of a small device with an LCD display), or behind-the-ear - similar to a hearing aid. The speech processor receives information about ambient sounds from the microphone, analyzes and encodes it. This information is then transmitted to the second component of the system, cochlear implant.
There are several models of cochlear implants. The choice of a cochlear implant model is carried out by doctor based on the data of the preliminary examination.
Cochlear implant is designed to last a lifetime with no wear or replacement parts and no maintenance.
How Cochlear Implant Works
The sounds of the world around us are picked up by a directional microphone located behind the ear. The sensitivity of the microphone can be changed by patient independently while using the speech processor.
The speech processor receives information about sounds from the microphone in the form of electrical signals.
The speech processor performs frequency analysis and selection of this information, and encodes it.
Sound information is encoded according to the speech coding strategy - it is selected at the individual setting of the speech processor for each patient and reflects his individual needs.
Encoded audio information is transmitted from the speech processor to the transmitter coil.
From the transmitter coil, the encoded signals in the form of radio waves are transmitted through the skin to the receiver / stimulator, in which the encoded information is transformed into electrical impulses.
Electrical impulses through the electrode array enter the inner ear, where the fibers of the cochlear nerve are stimulated.
Through the cochlear nerve, sound information is transmitted to the brain, where it is perceived as sound.
-
Procedure Duration
2-3 hours
-
Hospital Stay
5-7 days
It is important to understand that cochlear implantation is not only a surgical operation, but a complex method of rehabilitation for children and adults with deafness and severe hearing loss, carried out by a team of specialists, including audiologists, otosurgeons, teachers of the deaf , psychologists, engineers, physiologists, etc.
Cochlear implantation is not a one-time action, but a complex, multi-stage method of rehabilitation, which consists of 3 main stages:
The first stage is a preliminary examination of patient, determination of the possibility of cochlear implantation. At this stage, questions about the effectiveness and necessity of cochlear implantation are resolved individually for each patient.
The second stage is surgery. During the operation, the body of the implant is placed under the skin behind the human ear, and the electrode array emerging from the body is inserted into the cochlea. Cochlear implantation operation usually takes about two hours and is not technically difficult. A month after the operation, a small scar remains behind the ear, which is hidden by the hair.
The third stage of cochlear implantation is rehabilitation. 4-6 weeks after the operation, the speech processor is connected to the cochlear implant and the initial adjustment of the speech processor is performed. From this point on, patient can enjoy the benefits of cochlear implant and hear sounds. At this stage, the speech processor is tuned, the speech coding strategy is selected, and individual listening programs are created to obtain the maximum effect for the cochlear implant user. This work is aimed at the formation of full-fledged auditory sensations in a person. At the third stage, classes with a teacher of the deaf begin with the aim of developing speech function.
Bilateral deep sensorineural deafness (the average threshold of auditory perception at frequencies.
The thresholds of hearing perception in a free sound field when using optimally matched hearing aids.
The absence of a pronounced improvement in the auditory perception of speech from the use of optimally matched hearing aids with a high degree of bilateral sensorineural hearing loss, at least after using devices for 3-6 months (in children who have had meningitis, this gap can be reduced).
Lack of cognitive problems.
Lack of psychological problems.
The absence of serious concomitant somatic diseases.
The presence of serious support from parents and their readiness for a long postoperative rehabilitation period of training the implanted patient with audiologists and teachers of the deaf.
Complete or partial, but significant, obliteration of the cochlea.
Retrocochlear pathology (damage to the auditory nerve, neuroma of the cochlear nerve, etc.).
Negative results of the promontory test.
Concomitant severe somatic diseases (chronic renal failure, decompensated heart defects, etc.).
Intellectual disability.
The presence of focal pathology in the cortical or subcortical structures of the brain.
Lack of desire for many years of work with a teacher of the deaf after implantation (in adults) or lack of support from family members and their readiness for long-term rehabilitation work.
Cochlear implantation can be performed at any age, starting from 7 months in the absence of contraindications.
For children with congenital deafness and hearing loss in the first year of life, optimal results can be achieved before the age of 2 years.
For older children and adults, the issue of cochlear implantation should be decided individually, taking into account medical, psychological and social indicators.
In adults, maximum age is limited by general health.
Consultation with an audiologist - determining the effectiveness of hearing aids and a person's need for cochlear implantation.
Electroencephalography with the consultation of a neuropathologist - identification of history of epilepsy and other interfering reasons, cochlear implantation.
Otoneurologist's consultation - conclusion on indications for cochlear implantation.
Consultation of an ENT doctor - conclusion about the condition of the middle ear, eardrum, identification of other reasons that impede the operation.
Audiometry - determination of hearing thresholds.
Acoustic impedance measurement - conclusion about the function of the middle ear.
Study of evoked otoacoustic emission - conclusion on the function of the cochlea.
Study of auditory evoked potentials - conclusion about the preservation of the function of the cochlear nerve and the central parts of the auditory analyzer.
Promontorial testing - conclusion about the presence of functionally intact auditory nerve fibers.
Magnetic resonance imaging of the temporal bones.
Computed tomography of the temporal bones - conclusion about the patency of the tympanic ladder of the cochlea.