About Treatment
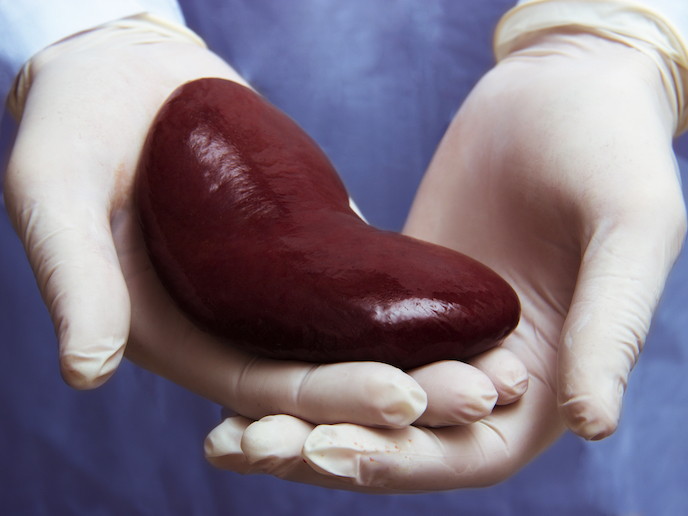
Kidney transplantation is a surgical operation that involves the transplantation of a kidney from another person to a person. It is used as a method of renal replacement therapy in end-stage chronic renal failure
The main criteria for the selection of a donor kidney are the correspondence of blood groups, HLA antigens (different forms of the same gene), approximate correspondence of the weight and age of donor and recipient. In some cases, operations are performed without taking into account the blood group. Donors should not be carriers of vector-borne (i.e. blood-borne) infections (syphilis, HIV, hepatitis B, C).
Operation
Before transplantation, patient is given general anesthesia intravenously in the arm or hand, and then inhalation anesthesia. It maintains sleep throughout the entire operation and blocks any pain. The operation takes 1.5 - 3 hours.
First, doctor makes an incision 2 fingers above the pubis and prepares the site for the graft. The donor kidney will be sutured to the artery and vein, and the ureter (the muscle tube through which urine flows) to the bladder.
During kidney transplantation, a catheter is placed in the bladder. This is necessary to drain urine and reduce the pressure in the bladder if the kidney is working too hard. The catheter may cause burning sensation in the urethra or urge to urinate.
During surgery, a disposable ureteral stent is sometimes placed to reduce the risk of complications. It is a tube fixed at one end in the pelvis of the transplanted kidney, and at the other in the bladder. The stent is removed 14-30 days after surgery. For this, cystoscopy is performed.
Immediately after operation
Immediately after the operation, patient is transferred to the intensive care unit. The room is specially equipped for the early postoperative period. Patient remains in hospital for another 1-3 weeks. In case of complications, the stay may be extended.
During the recovery period, patient needs:
the next day after the operation, get out of bed and start moving around;
turn in bed every hour, breathe deeply and cough 10-20 times an hour;
take immunosuppressive drugs.
Patient after kidney transplant should take these drugs throughout their life with the transplant - they reduce the likelihood of rejection of the new kidney.
-
Operation Duration
1,5-3 hours
-
Hospital Stay
10-15 days
The indication for kidney transplantation is end-stage chronic renal failure - the final stage of the course of chronic glomerulonephritis, chronic pyelonephritis, diabetic nephropathy, polycystic kidney disease, trauma and urological diseases, congenital kidney diseases. Patients with ESRD are on renal replacement therapy (RRT), which includes chronic hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis, and kidney transplantation, to save life. Kidney transplantation, in comparison with the other two options, has the best results in terms of life expectancy (increasing it by 1.5-2 times compared to other options for renal replacement therapy), and its quality.
Chronic kidney disease
Acute renal failure
Age less than 18 and over 70
Oncological diseases
Bacterial sepsis
Detection of HBsAg and HCV, HIV
Kidney transplantation can increase life expectancy, reduce the severity of pathological manifestations, improve the quality of life, facilitate social and medical rehabilitation of patients with end-stage renal failure, as well as reduce the cost of treating this category of patients. Kidney transplantation is a surgical procedure that carries certain anesthetic and surgical risks. In addition, due to the need for long-term immunosuppressive therapy in the postoperative period, there may be side effects associated with suppression of the immune system. At the stage of preoperative preparation of patient, potential contraindications for transplantation are assessed, as well as risk factors (for example, the risk of malignant neoplasms and infectious complications).
Rehabilitation begins immediately after the transplant operation. The process of donor kidney engraftment in patient's body is influenced by the quality of the material, the pathology that caused the need for transplantation, as well as the correct organization of subsequent therapy.
If complications do not arise after the operation, then the donor organ begins to work correctly after five to ten days. Basically, the complete restoration of functions occurs after the completion of the anastomoses, and the final normalization of the state of health and the absence of manifestations of kidney failure may take up to several weeks.